TIVA – Total Intravenous Anesthesia
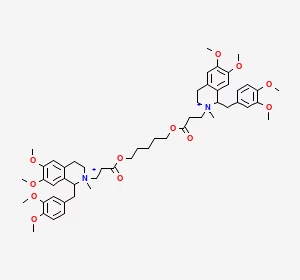
TIVA uses IV agents (propofol + remifentanil) for anesthesia without inhalational gases. Regimens: Propofol (TCI 2–6 mcg/mL or 100–200 mcg/kg/min) + remifentanil (TCI 2–6 ng/mL or 0.05–0.3 mcg/kg/min). Monitoring: BIS (40–60) ensures depth. Ideal for MH risk, PONV-prone patients, or neurosurgery. Enables precise titration and rapid emergence.