Anesthesia Machine & Anesthesia Workstation
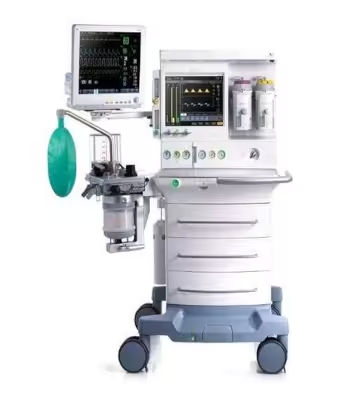 Welcome to the nerve center of the operating room. The anesthesia workstation, with its complex array of dials, circuits, and monitors, can seem like an intimidating beast. But what if you could master it? This comprehensive resource is your guide on a fascinating journey—from the historic, clunky elegance of the Boyle's machine to the sleek, intelligent workstations of Dräger, GE, and Mindray that define modern practice. We will demystify the physics, deconstruct the components, and build your confidence. This isn't just about learning a machine; it's about understanding your most critical partner in ensuring patient safety.
Welcome to the nerve center of the operating room. The anesthesia workstation, with its complex array of dials, circuits, and monitors, can seem like an intimidating beast. But what if you could master it? This comprehensive resource is your guide on a fascinating journey—from the historic, clunky elegance of the Boyle's machine to the sleek, intelligent workstations of Dräger, GE, and Mindray that define modern practice. We will demystify the physics, deconstruct the components, and build your confidence. This isn't just about learning a machine; it's about understanding your most critical partner in ensuring patient safety.
Our journey will be a methodical one. We'll start by laying a strong foundation, exploring the history and the core physics that govern every machine. From there, we'll build up your knowledge piece by piece, dissecting the classic anatomy of an anesthesia machine and mastering the circle breathing system. Only then will we leap into the modern era, comparing the sophisticated features of today's leading workstations. Each module is designed to build upon the last, transforming a daunting subject into a clear, manageable, and ultimately, masterable skill.
Isoflurane
Isoflurane is a potent, reliable inhalational anesthetic (MAC ~1.2%) with moderate blood solubility (λB:G 1.4). Known for cardiovascular stability and bronchodilation, it uses a standard vaporizer. Pungent but less than Desflurane; suitable for pediatric maintenance. Cost-effective with minimal metabolism, making it a staple in anesthesia practice.
Desflurane

Desflurane is a potent inhalational anesthetic prized for its rapid emergence due to low blood solubility (MAC 6-7%). Ideal for outpatient surgery and fast wake-up needs. Requires a special heated vaporizer. Pungent and irritating, it’s contraindicated for inhalational induction. Minimal metabolism offers low toxicity risk. Key for anesthesia efficiency.
Sevoflurane

Sevoflurane is a potent, non-pungent inhalational anesthetic (MAC ~2%) with low blood solubility (λB:G 0.65). Ideal for smooth inhalational induction (especially pediatrics) and rapid emergence. Uses a standard vaporizer. Minimal airway irritation; monitor for Compound A with low-flow anesthesia. Low metabolism ensures safety.
Midazolam
Midazolam is a short-acting benzodiazepine used for preoperative sedation, anxiolysis, and amnesia. Rapid IV onset (1-2 min), metabolized hepatically. Causes respiratory depression; requires reversal with flumazenil. Synergistic with opioids. Key for procedural sedation and anxiolysis in anesthesia.
Anesthetic Emergencies
Divine Debut of Anesthesia?
The scriptures of major religions do not explicitly describe the use of modern anesthesia, as the concept and technology of anesthesia are relatively recent developments in human history. However, there are instances in religious texts that describe states of deep sleep, unconsciousness, or divinely induced trances that could be interpreted…
Anesthesia Techniques
Anesthesiologists employ various techniques and medications to administer anesthesia, tailoring their approach based on the patient’s medical condition, the nature of the surgery, and the desired depth of anesthesia. The primary goal is to induce a state of unconsciousness or analgesia (pain relief) while maintaining physiological stability. Here are some…
Thiopentone Sodium
Disclaimer!
The information provided on this platform, including but not limited to articles, case studies, clinical scenarios, guidelines, and multimedia content, is intended for educational and informational purposes only.
The authors and editors of this material have made every effort to ensure the accuracy of treatments, drugs, and dosage regimens that conform to currently accepted standards. However, due to continual changes in information resulting from ongoing research and clinical experience, unique aspects of individual clinical situations, as well as the potential for human error; readers must exercise personal judgment when making a clinical decision.
This website may contain third-party information or links to other internet websites. We do not control nor assume responsibility for any third-party content provided nor content on linked Internet websites.
We strongly recommend the visitors of this website to go through its Detailed 'Disclaimer' and 'Terms of Use'.
By accessing, browsing, or using this website, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agreed to be bound by the 'Disclaimer' and 'Terms of Use'. If you do not agree with these terms, you must NOT use this website.