Anesthesia Machine & Anesthesia Workstation
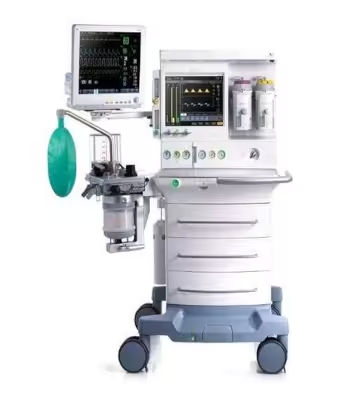 Welcome to the nerve center of the operating room. The anesthesia workstation, with its complex array of dials, circuits, and monitors, can seem like an intimidating beast. But what if you could master it? This comprehensive resource is your guide on a fascinating journey—from the historic, clunky elegance of the Boyle's machine to the sleek, intelligent workstations of Dräger, GE, and Mindray that define modern practice. We will demystify the physics, deconstruct the components, and build your confidence. This isn't just about learning a machine; it's about understanding your most critical partner in ensuring patient safety.
Welcome to the nerve center of the operating room. The anesthesia workstation, with its complex array of dials, circuits, and monitors, can seem like an intimidating beast. But what if you could master it? This comprehensive resource is your guide on a fascinating journey—from the historic, clunky elegance of the Boyle's machine to the sleek, intelligent workstations of Dräger, GE, and Mindray that define modern practice. We will demystify the physics, deconstruct the components, and build your confidence. This isn't just about learning a machine; it's about understanding your most critical partner in ensuring patient safety.
Our journey will be a methodical one. We'll start by laying a strong foundation, exploring the history and the core physics that govern every machine. From there, we'll build up your knowledge piece by piece, dissecting the classic anatomy of an anesthesia machine and mastering the circle breathing system. Only then will we leap into the modern era, comparing the sophisticated features of today's leading workstations. Each module is designed to build upon the last, transforming a daunting subject into a clear, manageable, and ultimately, masterable skill.
Neostigmine
The standard reversal agent for non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockade, Neostigmine inhibits acetylcholinesterase. It requires mandatory co-administration with an anticholinergic to prevent bradycardia and secretions. Objective confirmation of adequate reversal with a nerve stimulator is essential before considering extubation.
Tramadol
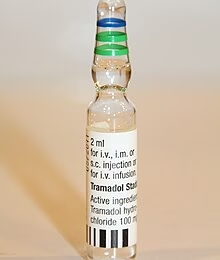
An atypical opioid for moderate pain, Tramadol has a dual mechanism: weak µ-opioid agonism and serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. This creates unique risks of seizures and serotonin syndrome. Meticulous medication review is essential before use, as it is not a benign alternative to traditional opioids.
Naloxone

The essential opioid antagonist, Naloxone rapidly reverses life-threatening respiratory depression. Its short half-life demands vigilant monitoring for re-sedation, as its effects wear off before the opioid’s. In dependent patients, it precipitates severe withdrawal, causing pain and hemodynamic instability.
Morphine
Fentanyl
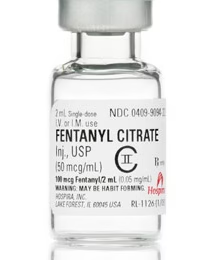
A cornerstone of anesthesia, Fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid offering profound analgesia and hemodynamic stability. Its primary danger is rapid-onset respiratory depression and chest wall rigidity. Meticulous dosing and continuous respiratory monitoring are critical to prevent life-threatening complications.
Epsilon Amino Caproic Acid (EACA)

Epsilon Amino Caproic Acid is a fundamental antifibrinolytic agent used to stabilize clots and reduce bleeding in high-risk surgical and trauma patients. While highly effective, its use requires careful patient selection, vigilant monitoring for thrombosis and renal dysfunction, and dose adjustment in renal impairment.
IV Giving Sets & Burettes
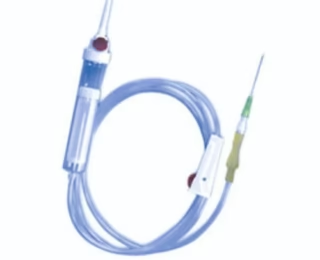
In anesthesia, IV giving sets are lifelines, not just tubes. The anesthesiologist selects them deliberately—from standard sets to rapid infusers—for precise fluid and drug delivery. The burette provides critical control for small-volume needs, especially in pediatrics, ensuring meticulous management of the patient’s hemodynamic state.
Syringes
Disclaimer!
The information provided on this platform, including but not limited to articles, case studies, clinical scenarios, guidelines, and multimedia content, is intended for educational and informational purposes only.
The authors and editors of this material have made every effort to ensure the accuracy of treatments, drugs, and dosage regimens that conform to currently accepted standards. However, due to continual changes in information resulting from ongoing research and clinical experience, unique aspects of individual clinical situations, as well as the potential for human error; readers must exercise personal judgment when making a clinical decision.
This website may contain third-party information or links to other internet websites. We do not control nor assume responsibility for any third-party content provided nor content on linked Internet websites.
We strongly recommend the visitors of this website to go through its Detailed 'Disclaimer' and 'Terms of Use'.
By accessing, browsing, or using this website, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agreed to be bound by the 'Disclaimer' and 'Terms of Use'. If you do not agree with these terms, you must NOT use this website.