Anesthesia Machine & Anesthesia Workstation
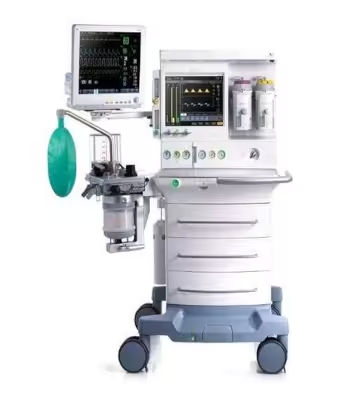 Welcome to the nerve center of the operating room. The anesthesia workstation, with its complex array of dials, circuits, and monitors, can seem like an intimidating beast. But what if you could master it? This comprehensive resource is your guide on a fascinating journey—from the historic, clunky elegance of the Boyle's machine to the sleek, intelligent workstations of Dräger, GE, and Mindray that define modern practice. We will demystify the physics, deconstruct the components, and build your confidence. This isn't just about learning a machine; it's about understanding your most critical partner in ensuring patient safety.
Welcome to the nerve center of the operating room. The anesthesia workstation, with its complex array of dials, circuits, and monitors, can seem like an intimidating beast. But what if you could master it? This comprehensive resource is your guide on a fascinating journey—from the historic, clunky elegance of the Boyle's machine to the sleek, intelligent workstations of Dräger, GE, and Mindray that define modern practice. We will demystify the physics, deconstruct the components, and build your confidence. This isn't just about learning a machine; it's about understanding your most critical partner in ensuring patient safety.
Our journey will be a methodical one. We'll start by laying a strong foundation, exploring the history and the core physics that govern every machine. From there, we'll build up your knowledge piece by piece, dissecting the classic anatomy of an anesthesia machine and mastering the circle breathing system. Only then will we leap into the modern era, comparing the sophisticated features of today's leading workstations. Each module is designed to build upon the last, transforming a daunting subject into a clear, manageable, and ultimately, masterable skill.
Tele-Anesthesia and Remote Monitoring

Tele-anesthesia leverages high-speed networks and AI to deliver expert anesthesia care from a distance. From a central command center, anesthesiologists can provide real-time oversight for multiple operating rooms, enhancing patient safety and democratizing access to specialist expertise in rural hospitals and ambulatory surgery centers.
Ambulatory and Portable Anesthesia

The practice of anesthesia has decisively moved beyond the traditional hospital operating room, driven by a demand for efficiency, patient comfort, and advanced technology. This evolution has given rise to two critical subspecialties: Ambulatory Anesthesia, focused on rapid recovery for same-day surgery, and Portable Anesthesia, which brings a fully-equipped, mobile anesthetic suite to non-traditional locations like MRI rooms, endoscopy clinics, and dental offices.
Bispectral Index (BIS) Monitor
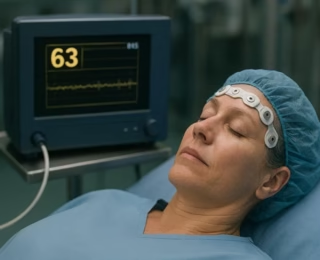
The BIS monitor analyzes brain EEG waves to create a single number (0-100) indicating a patient’s consciousness level. It helps clinicians precisely titrate anesthetic drugs, preventing intraoperative awareness while avoiding oversedation, leading to safer, faster recovery for patients undergoing surgery or sedation.
Cardiac Output Monitor

Minimally invasive monitors like FloTrac and EV1000 analyze arterial waveforms to deliver continuous cardiac output data. This real-time insight is vital for guiding fluid and drug therapy in critically ill patients, offering a powerful, less-risky alternative to traditional pulmonary artery catheters for hemodynamic management.
Automated Anesthesia Delivery Systems (“Anesthesia Robots”)
Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy (GDFT)
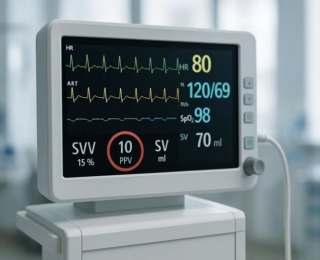
Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy (GDFT) is a modern, evidence-based approach that marks a fundamental shift from traditional fluid management. Instead of relying on static, often misleading parameters like central venous pressure (CVP), GDFT uses real-time, dynamic monitoring to personalize fluid delivery for each patient.
Opioid-Sparing and Opioid-Free Anesthesia (OFA)
Opioid-Sparing and Opioid-Free Anesthesia uses a multimodal approach—combining regional blocks and IV medications like ketamine and lidocaine—to minimize opioid use. This strategy reduces side effects like nausea and ileus, leading to faster recovery and less risk of chronic postoperative pain.
Postoperative Delirium and Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction
Disclaimer!
The information provided on this platform, including but not limited to articles, case studies, clinical scenarios, guidelines, and multimedia content, is intended for educational and informational purposes only.
The authors and editors of this material have made every effort to ensure the accuracy of treatments, drugs, and dosage regimens that conform to currently accepted standards. However, due to continual changes in information resulting from ongoing research and clinical experience, unique aspects of individual clinical situations, as well as the potential for human error; readers must exercise personal judgment when making a clinical decision.
This website may contain third-party information or links to other internet websites. We do not control nor assume responsibility for any third-party content provided nor content on linked Internet websites.
We strongly recommend the visitors of this website to go through its Detailed 'Disclaimer' and 'Terms of Use'.
By accessing, browsing, or using this website, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agreed to be bound by the 'Disclaimer' and 'Terms of Use'. If you do not agree with these terms, you must NOT use this website.